Your Anthropogenic climate change definition ipcc images are ready in this website. Anthropogenic climate change definition ipcc are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Anthropogenic climate change definition ipcc files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for anthropogenic climate change definition ipcc images information related to the anthropogenic climate change definition ipcc keyword, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
Anthropogenic Climate Change Definition Ipcc. Anthropogenic Climate Change Jens Hesselbjerg Christensen Danish Climate Centre Danish Meteorological Institute Lyngbyvej 100 DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø Denmark Email. Climate change means a change of climate which is. On Climate Change IPCC WGIWGII on Detection and Attribution related to Anthropogenic Climate Change which was held in Geneva Switzerland on 14-16 September 2009. CC0 Public Domain Scientific support for the link.
 Climate Change Emergency Medical Response From climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Climate Change Emergency Medical Response From climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Responses eg regional climate change. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution humans have engaged in a range of behaviors eg burning fossil fuels as an energy source and deforestation that have increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Jhcdmidk Scientific understanding of anthropogenic global climate change has advanced notably in recent years and led to commensurate developments of mitigation strategies. Scientific consensus is that these behaviors are interrupting the carbon cycle and contributing to long. Anthropogenic emissions Emissions of greenhouse gases GHGs precursors of GHGs and aerosols caused by human activities. When a pattern of extreme weather persists for some.
Human-induced warming of the climate system is widespread.
A change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods. Carbon neutrality is achieved when anthropogenic CO2 emissions are balanced globally by anthropogenic carbon dioxide removals over a specified period. A major component of anthropogenic climate change is global warming which refers to a gradual warming of the earth caused by an unnatural human-induced increase of the greenhouse effect as concentrations of greenhouse gases increase primarily from the burning of fossil fuels coal oil and natural gas. Note that the Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC in its Article 1 defines climate change as. Carbon neutrality is also referred to as net-zero carbon dioxide emission. The simple formulae used by the IPCC to calculate the radiative forcing due to well-mixed greenhouse gases have been improved leading to a slight change in the forcing estimates.

United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC. Physical environment or biota resulting from climate change which have significant deleterious effects on the composition resilience or productivity of natural and managed ecosystems or on the operation of socio-economic systems or on human health and welfare. Contemporary climate change includes both the global warming caused by humans and its impacts on Earths weather patterns. Human-induced warming of the climate system is widespread. Multi-signal detection and attribution analyses which quantify the contributions of different natural and anthropogenic forcings to observed changes show that.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Compared to the use of the earlier expressions the improved formulae for fixed changes in gas concentrations. Note that the Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC in its Article 1 defines climate change as. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earths energy balance. It seeks to clarify methods definitions and terminology across the two working groups and is intended as a guide for future IPCC Lead Authors. Impacts Adaptation and Vulnerability Part B.
 Source: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Here we build on the expert judgement-based assessment by the intergovernmental panel on climate change ipcc 5 6 to estimate the composite risk from anthropogenic climate change by the end of. Anthropogenic Climate Change Jens Hesselbjerg Christensen Danish Climate Centre Danish Meteorological Institute Lyngbyvej 100 DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø Denmark Email. The planet faces a bleak prognosis unless drastic actions are undertaken immediately. Adjustment in natural or human systems in response to actual. The conclusions of the IPCC are the other most often cited support for anthropogenic climate change.
 Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Jhcdmidk Scientific understanding of anthropogenic global climate change has advanced notably in recent years and led to commensurate developments of mitigation strategies. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC is active socially choose your network. Contemporary climate change includes both the global warming caused by humans and its impacts on Earths weather patterns. These activities include the burning of fossil fuels deforestation land use. 14 System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts encompassing other factors.
 Source: dw.com
Source: dw.com
Since the start of the Industrial Revolution humans have engaged in a range of behaviors eg burning fossil fuels as an energy source and deforestation that have increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. A change of climate which is. Anthropogenic Climate Change Jens Hesselbjerg Christensen Danish Climate Centre Danish Meteorological Institute Lyngbyvej 100 DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø Denmark Email. The simple formulae used by the IPCC to calculate the radiative forcing due to well-mixed greenhouse gases have been improved leading to a slight change in the forcing estimates. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution humans have engaged in a range of behaviors eg burning fossil fuels as an energy source and deforestation that have increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
 Source: dw.com
Source: dw.com
Carbon neutrality is achieved when anthropogenic CO2 emissions are balanced globally by anthropogenic carbon dioxide removals over a specified period. Jhcdmidk Scientific understanding of anthropogenic global climate change has advanced notably in recent years and led to commensurate developments of mitigation strategies. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution humans have engaged in a range of behaviors eg burning fossil fuels as an energy source and deforestation that have increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. See also Anthropogenic emissions and Anthropogenic removals. Climate change may be due to natural internal processes or external forcings such as modulations of the solar cycles volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
IPCC Anthropogenic climate change. When a pattern of extreme weather persists for some. Note that the Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC in its Article 1 defines climate change as. Radiative forcing is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts metre2. A change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods The UNFCCC thus makes a.
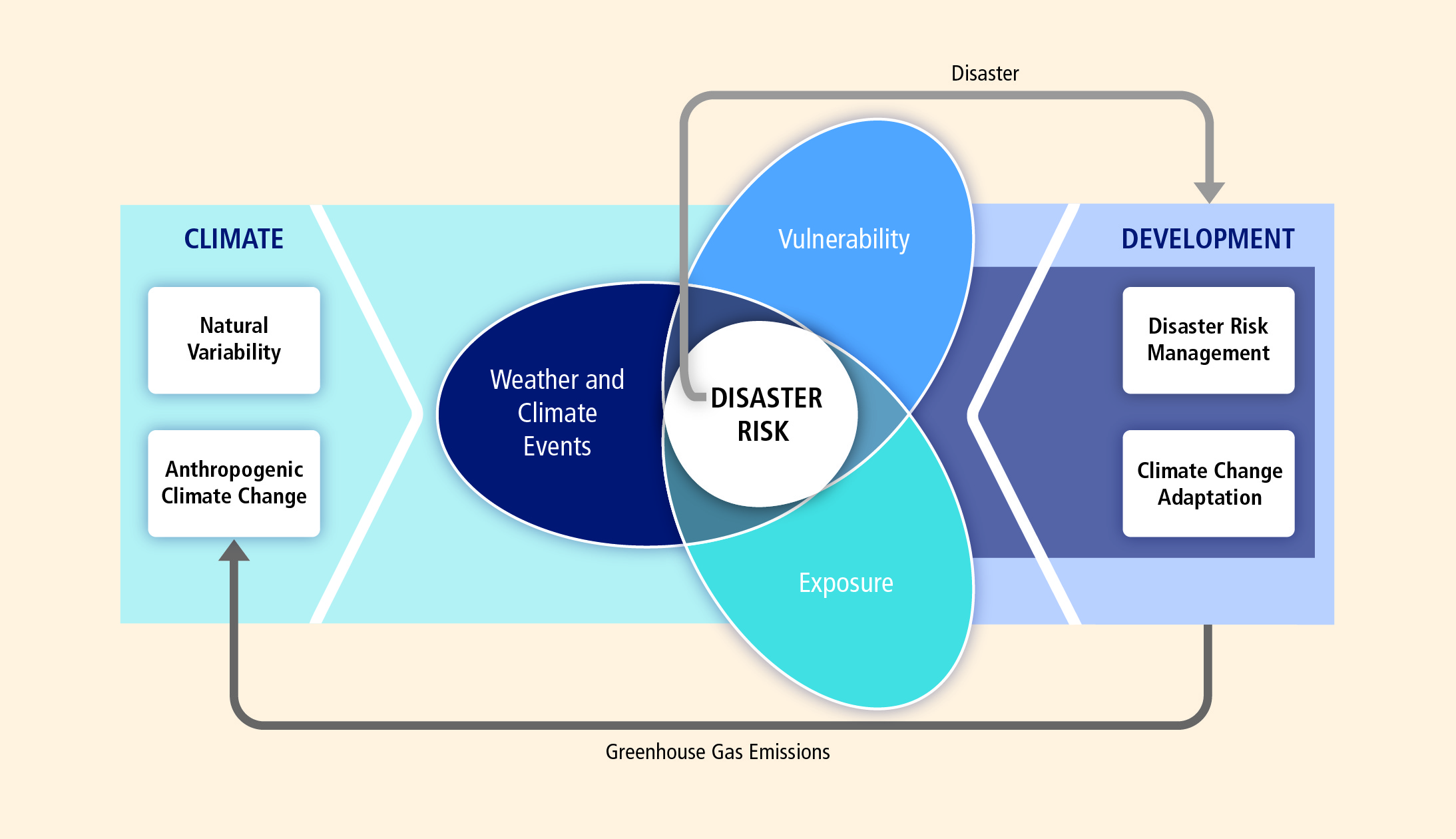 Source: ipcc.ch
Source: ipcc.ch
The planet faces a bleak prognosis unless drastic actions are undertaken immediately. A change of climate which is. Anthropogenic Climate Change Jens Hesselbjerg Christensen Danish Climate Centre Danish Meteorological Institute Lyngbyvej 100 DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø Denmark Email. 1 The most recent document released by the IPCC summarizes the consequences of climate change and proposes potential avenues for. Multi-signal detection and attribution analyses which quantify the contributions of different natural and anthropogenic forcings to observed changes show that.
 Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
A change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods. Impacts Adaptation and Vulnerability Part B. It refers to any change in. Note that the Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC in its Article 1 defines climate change as. It seeks to clarify methods definitions and terminology across the two working groups and is intended as a guide for future IPCC Lead Authors.
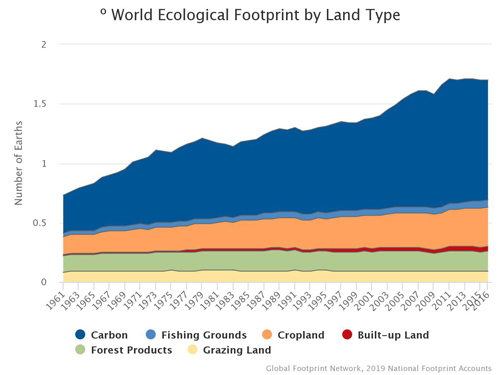 Source: footprintnetwork.org
Source: footprintnetwork.org
There have been previous periods of climate change but the current changes are more rapid than any known events in Earths history. A change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods The UNFCCC thus makes a. These activities include the burning of fossil fuels deforestation land use. Human-induced warming of the climate system is widespread. Anthropogenic Contributors to Climate Change.
 Source: dw.com
Source: dw.com
On Climate Change IPCC WGIWGII on Detection and Attribution related to Anthropogenic Climate Change which was held in Geneva Switzerland on 14-16 September 2009. Impacts Adaptation and Vulnerability Part B. The simple formulae used by the IPCC to calculate the radiative forcing due to well-mixed greenhouse gases have been improved leading to a slight change in the forcing estimates. 14 System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts encompassing other factors. Note that the Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC in its Article 1 defines climate change as.
 Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Climate change may be due to natural internal processes or external forcings such as modulations of the solar cycles volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use. A change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods The UNFCCC thus makes a. Here we build on the expert judgement-based assessment by the intergovernmental panel on climate change ipcc 5 6 to estimate the composite risk from anthropogenic climate change by the end of. Anthropogenic Resulting from or produced by human activities. The planet faces a bleak prognosis unless drastic actions are undertaken immediately.
 Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Source: climate-change-emergency-medical-response.org
Using statistical tests by changes in the mean andor the variability of its properties and that persists for an extended period typically decades or longer. Impacts Adaptation and Vulnerability Part B. Climate change may be due to natural internal processes or external forcings such as modulations of the solar cycles volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use. Reports AR5 Climate Change 2014. Human-induced warming of the climate system is widespread.
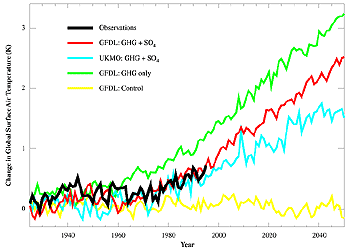 Source: archive.ipcc.ch
Source: archive.ipcc.ch
Anthropogenic emissions Emissions of greenhouse gases GHGs precursors of GHGs and aerosols caused by human activities. Climate change may be due to natural internal processes or external forcings such as modulations of the solar cycles volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use. CC0 Public Domain Scientific support for the link. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC is active socially choose your network. These activities include the burning of fossil fuels deforestation land use.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Note that the Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC in its Article 1 defines climate change as. Adjustment in natural or human systems in response to actual. IPCC Anthropogenic climate change. Anthropogenic climate change caused significant ecosystem shifts and species extinctions during the past millions of years high confidence8 Based on many studies covering a wide range of regions and crops negative impacts of climate change on crop yields have been more. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution humans have engaged in a range of behaviors eg burning fossil fuels as an energy source and deforestation that have increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
 Source: mei.edu
Source: mei.edu
The planet faces a bleak prognosis unless drastic actions are undertaken immediately. Anthropogenic warming of the climate system can be detected in temperature observations taken at the surface in the troposphere and in the oceans. Using statistical tests by changes in the mean andor the variability of its properties and that persists for an extended period typically decades or longer. This paper also outlines guidelines for how to assess. So concludes the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes IPCCs Fifth Assessment Report completed over the course of 2014.

These activities include the burning of fossil fuels deforestation land use. Jhcdmidk Scientific understanding of anthropogenic global climate change has advanced notably in recent years and led to commensurate developments of mitigation strategies. Adjustment in natural or human systems in response to actual. By definition the characteristics of what is called extreme weather may vary from place to place in an absolute sense. Since the start of the Industrial Revolution humans have engaged in a range of behaviors eg burning fossil fuels as an energy source and deforestation that have increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
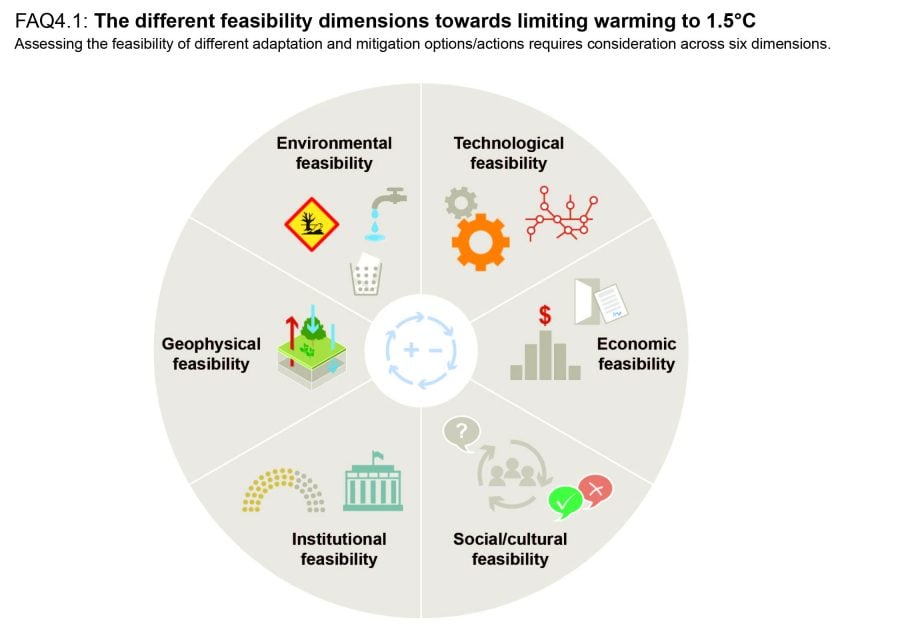 Source: ipcc.ch
Source: ipcc.ch
1 The most recent document released by the IPCC summarizes the consequences of climate change and proposes potential avenues for. By Institute of Physics. A major component of anthropogenic climate change is global warming which refers to a gradual warming of the earth caused by an unnatural human-induced increase of the greenhouse effect as concentrations of greenhouse gases increase primarily from the burning of fossil fuels coal oil and natural gas. So concludes the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes IPCCs Fifth Assessment Report completed over the course of 2014. Reports AR5 Climate Change 2014.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title anthropogenic climate change definition ipcc by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






